Suborder COTYLEA
Superfamily PSEUDOCEROTOIDEA
Family PSEUDOCEROTIDAE
Genus ACANTHOZOON
Species LEPIDUM
Literature reference:
Original description:
Heath, H. & McGregor, EA. 1912. New
polyclads from Monterey Bay, California.
Proc. Acad. nat. Sci. Philadelphia, 64:455-
488.
Other:
du Bois-Reymond Marcus, E. 1955, on Turbellaria and Polygordius from the Brazilian coast.
Bol. Fac. Filos. Cienc.Univ. S. Paulo No. 207 (Zool. No. 20): 19-65.
Synonymy:
Licheniplana lepida Heath & McGregor
1912
Pseudoceros (Acanthozoon) lepida du Bois-Reymond Marcus 1955
Description:
Form:
Broad oval to 12 mm. in length by 8 mm.in width. There are small papillae on the dorsal surface being more numerous on the anterior part of the worm. The brain is located about half the distance between the anterior margin and the mouth. The ventral sucker is located slightly posterior to the midpoint of the body.
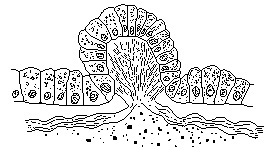
Acanthozoom lepidium Figure 2. Section through dorsal papilla
(after Heath & McGregor). Click to enlarge.
Color:
The dorsal surface is white, gray or lead color with small pinkish or dark red pigment spots. The ventral surface is unpigmented.

Acanthozoom lepidium Figure 4. Enlarged view of the eyes (after Heath & McGregor). Click to enlarge.
Eyes:
Marginal eyes in two indefinite clusters between the marginal tentacles. The two clusters of cerebral eyes, numbering about 15 each, are located in the area over the brain.
Digestive system:
The mouth opens to a ruffled pharynx that leads to the main intestine which is reported to have approximately 50 pairs of lateral branches.The lateral branches subdivide forming a highly anastomosing network.
Copulatory apparatus:
The sperm ducts anastomose and then fuse to form the spermiducal vesicles which are lateral to the main intestine and extend anteriorly from almost its posterior extent. At a point slightly posterior to the pharynx the spermiducal vesicles curve medially and enter separately the spherical seminal vesicle. The ejaculatory duct exits the anterior end of the seminal vesicle and bends backward and curves ventral and then anterior to enter the base of the short conical penis. The short prostatic duct joins the ejaculatory duct prior to its entrance into the base of the penis. The prostatic vesicle is a small oval body that occupies a space anteriorly between the seminal vesicle and the base of the penis papilla. The penis papilla is surrounded by a penis sheath that is directed anteriorly. The male antrum exits by the male gonopore which is located ventral to the posterior part of the pharynx. The female gonopore is located a short distance posterior to the male gonopore and leads to the vagina. The vagina gives rise to the paired uteri which extend laterally beyond the main intestine and then subdivide into an anterior branch which extends to a point opposite the mouth and a posterior branch extending to a point opposite the posterior end of the main intestine.

Acanthozoom lepidium Figure 3. Ventral view of the copulatory apparatus
(after Heath & McGregor). Anterior end to the top. Click to enlarge.
Distinguishing characteristics:
Small dorsal papilla; intestinal branches numerous; color.
Distribution:
Monterey Bay, California
Holotype location:
Unknown
Download PDF Document of this page
Download Word Document of this page

